
Why Men Should Focus on Gut Health
In recent years, the spotlight on gut health has intensified — drawing attention to just how important gut function is for overall mental and physical well-being.
| Table of Contents |
|
For men in particular, paying attention to gut health is not just about avoiding digestive issues like gas or abdominal pain, but also about improving nutrient absorption, energy, mental clarity, appetite control, libido, and immune defenses.
But why is this crucial? The human health part of the gut microbiome is deeply intertwined with hormonal balance, metabolic health, and physical performance, as well as many other essential bodily processes.
In this article, you'll learn about the importance of maintaining your gut health, especially as a man, including the connection between a well-functioning gut and healthy body composition and sex drive, as well as proactive steps that can lead to significant improvements in a man's quality of life thanks to their positive influence on the gut.
The Impact of Digestive Health on Men's Well-Being
Gut health refers to the balance and function of the bacteria and other microorganisms in the digestive and intestinal tract. When you think about "gut health," normal digestion might come to mind — but a healthy gut microbiome contributes to so much more than this, including:
● A strong immune system
● Heart health
● Sharper cognitive function
● Improved mood
● Restorative sleep
● Enhanced mental performance
● And more
Understanding the Gut Microbiome: Why Does It Matter?
The gut microbiome refers to the vast community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that reside in our digestive systems.
The balance of these microorganisms is essential for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, synthesizing certain vitamins, and protecting against pathogens. Disruptions to this delicate balance, known as dysbiosis, can lead to a variety of health issues, including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, diabetes, and even mental health disorders like anxiety and depression.
The relationship between gut health and overall well-being is a prime example of the body's interconnectedness.
An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to dysbiosis (when there are more harmful microbes in the gut than beneficial types), contributing to a range of issues from inflammation and weight gain to mental health challenges.
By recognizing the impact of your dietary choices, stress levels, and antibiotic use on your gut microbiome, you can take proactive steps toward nurturing this vital aspect of your health.
For instance, consuming a diverse diet rich in fiber, reducing stress, and being cautious with antibiotic use can all contribute to a healthier gut microbiome.
Benefits of a Healthy Gut

As research continues to uncover the vast influence of the gut microbiome on our health, it becomes increasingly clear that for men, taking care of their guts is one of the most effective ways to support men's health and overall well-being.
Here's more about the role that gut health can play in men's overall health:
Nutrient Absorption
The gut plays a pivotal role in nutrient absorption by breaking down foods into smaller constituent nutrients, which are then absorbed through the lining of the intestines into the bloodstream.
This process ensures that the body receives all the essential vitamins, minerals, and energy needed for all of its primary functions, including circulation, muscle protein synthesis, cognitive functions like learning and decision-making, and many others.
Hormonal Balance
The gut influences the regulation of hormones, including "hunger hormones" that regulate your appetite, insulin which is involved in energy metabolism and fat storage, and reproductive hormones such as testosterone. Dozens of different hormones are made inside the gut. Therefore, a healthy gut plays a vital role in muscle growth, fat distribution, and libido.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
The gut-brain axis is a two-way communication system that works via chemical messengers and nerve signaling. It describes the ability of the gut to impact a man's mood and cognitive functions, including how well he copes with stress and whether he experiences symptoms of anxiety and depression.
If a man deals with poor gut health, such as intestinal permeability (also known as leaky gut, in which the gut barrier becomes damaged and compromised) or malabsorption of essential nutrients, he's more susceptible to feeling burnt out, fatigued, and generally down. This has to do with a disruption in the production of neurotransmitters in the gut, including serotonin for example, which is a calming, "feel good" chemical.
Physical Performance
Nutrient absorption, which is vital for energy and recovery, is significantly influenced by gut health. A well-functioning gut supports optimal nutrition uptake and can enhance athletic performance, including stamina and strength. Additionally, a healthy gut-brain axis provides the motivation and energy needed for peak performance.
Immune Function and Defenses
A large portion of the immune system, up to 75%, is housed inside the gut, particularly in the gut lining and also within microbes that live in the gut and influence the production of protective white blood cells.
Maintaining a balanced gut flora is essential for defending the body against inflammation and pathogens and reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases, especially digestive ailments like GERD or heartburn, diabetes, autoimmune conditions, and certain types of cancer.
How Men Can Improve Their Gut Health
Improving gut and colon health is within reach for every man, although it involves effort, commitment, and often some lifestyle adjustments.
Here are five ways men can improve their internal ecosystem and gut health:
1. Diversify Your Diet, Including With Plenty of Fiber
Consuming a wide variety of foods, especially high-fiber foods like fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, can promote a balanced gut microbiome. These foods provide the nutrients that protective gut bacteria need to thrive, allowing them to ward off pathogens and harmful microbes that can lead to various health problems.
Aside from consuming enough fiber, which is about 30+ grams per day for adult men, men should focus on eating quality protein sources like fish and grass-fed meat, plus healthy fats that have anti-inflammatory effects, including nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Overall, when men include various types of foods in their diets, it helps ensure they're meeting their needs for vitamins and minerals that have been shown to beneficially modulate the gut microbiome — such as vitamins A, B2, D, E, C, and beta-carotene— which have roles including limiting inflammation, supporting microbial diversity, and increasing short-chain fatty acid production.
2. Incorporate Prebiotic and Probiotics
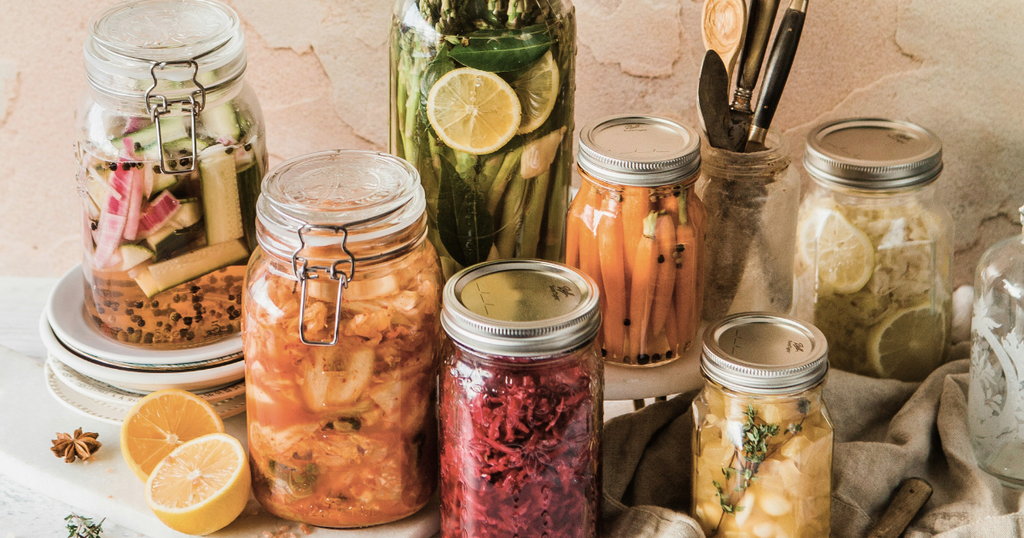

Probiotics, the friendly bacteria naturally found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha, play a pivotal role in maintaining gut health. These microorganisms have been linked to the treatment and prevention of various diseases, including digestive disorders and even mental health issues.
In parallel, prebiotics serve as nourishment for probiotic bacteria, fostering their growth and activity within the gut. Foods rich in prebiotics include bananas, onions, garlic, asparagus, and whole grains. Pairing prebiotic-rich foods with probiotic sources can amplify their benefits, contributing to a balanced and resilient gut microbiome.
You don't necessarily have to eat probiotics and prebiotics in the same meal. But try to incorporate both types into your regular diet by eating cultured/fermented foods and lots of different fibrous plants.
Prebiotic and Probiotic Supplements
While incorporating probiotics and prebiotics through dietary sources is ideal, it's not always convenient or feasible. In such cases, dietary supplements can provide a convenient and concentrated source of these essential elements for gut health.
When opting for probiotic supplements, look for those containing a diverse range of probiotic strains, as different strains offer distinct health benefits. Additionally, consider the potency and viability of the probiotic , ensuring they can survive the journey through the digestive tract to exert their effects in the gut.
Similarly, prebiotic fiber supplements are available in various forms, including powders, capsules, and chewable tablets. Select supplements that contain well-researched prebiotic fibers such as inulin, oligofructose, or galactooligosaccharides (GOS), which have demonstrated efficacy in supporting gut health.
3. Stay Hydrated and Avoid Too Much Alcohol
Drinking plenty of water has been shown to have a beneficial effect on the mucosal lining of the intestines, as well as on the balance of good bacteria in the gut. Staying hydrated and avoiding too much alcohol, which can have inflammatory and dehydrating effects, also prevents constipation and aids in detoxification.
Hydration and Gut Health:
-
Mucosal Integrity: The mucosal lining of the intestines acts as a barrier, protecting against harmful substances and pathogens while allowing for the absorption of nutrients. Adequate hydration supports the integrity of this lining, promoting its effectiveness as a protective barrier.
-
Balance of Gut Microbiota: Water plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Proper hydration helps create an environment conducive to the growth and proliferation of these beneficial microbes, which are essential for digestive health and immune function.
-
Digestive Efficiency: Hydration facilitates the movement of food through the digestive tract, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. This ensures the efficient elimination of waste and toxins from the body, supporting detoxification processes.
The Impact of Alcohol:
While moderate alcohol consumption may be okay, excessive intake can have detrimental effects on gut health:
-
Inflammatory Effects: Alcohol can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria and promote inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic inflammation is associated with an increased risk of digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
-
Dehydrating Effects: Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it increases urine production and can lead to dehydration if consumed in excess. Dehydration compromises the mucosal lining of the intestines, impairing its ability to function as an effective barrier against toxins and pathogens.
-
Digestive Disruption: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt normal digestive processes, leading to symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. It can also contribute to nutrient malabsorption and impaired liver function.
4. Sleep Enough and Manage Stress
Chronic stress can wreak havoc on gut health, leading to issues like inflammation and gut dysbiosis. Engaging in stress-reduction practices — such as regular exercise, meditation, reading, doing fun hobbies, socializing, and spending time outdoors — can all help you feel more relaxed, thereby aiding in a healthy gut-brain axis.
Sleep is another important aspect of mental and physical health, including gut microbiota function, since the body (including the brain and gut) repairs itself while you sleep. Clock in seven to nine hours of sleep most nights to feel your sharpest.
5. Avoid Unnecessary Antibiotics and OTC Drugs
While antibiotics and over-the-counter medications serve essential purposes in treating infections and managing symptoms, their indiscriminate use can have profound implications for gut health. Here's why it's crucial to use them judiciously:
The Impact of Antibiotics
-
Disruption of Gut Microbiota: Antibiotics are designed to target and eliminate harmful bacteria that cause infections. However, they can also inadvertently destroy beneficial bacteria in the gut, leading to a condition known as dysbiosis. Dysbiosis is characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiota and can manifest as digestive issues, such as bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort.
-
Potential Long-Term Effects: The effects of antibiotic use on gut health can extend beyond the duration of treatment. Research suggests that alterations in the gut microbiota caused by antibiotics may persist for weeks or even months after completing a course of antibiotics, predisposing individuals to ongoing digestive disturbances and other health complications.
-
Increased Risk of Antibiotic Resistance: Overuse and misuse of antibiotics contribute to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which pose a significant public health threat. By using antibiotics only when necessary and as prescribed by a healthcare provider, you can help mitigate the risk of antibiotic resistance and preserve the effectiveness of these life-saving medications.
Practical Tips for Responsible Antibiotic Use:
-
Follow Healthcare Provider's Instructions: Always take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Complete the full course of treatment, even if you start feeling better before it's finished, to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated.
-
Consider Alternatives: In some cases, antibiotics may not be the most appropriate treatment option. Discuss alternative approaches with your healthcare provider, such as watchful waiting or non-antibiotic treatments, when appropriate.
Rebuilding Gut Health
-
Probiotic Supplementation: After completing a course of antibiotics, consider taking a high-quality probiotic supplement daily to help restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
-
Probiotic-Rich Foods: In addition to supplements, incorporate probiotic-rich foods into your diet to help replenish beneficial bacteria in the gut and support digestive health.
-
Fiber-Rich Diet: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. Aim to consume plenty of fiber-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, to promote a optimal gut microbiota.
By using antibiotics and over-the-counter drugs responsibly and taking proactive steps to support gut health afterward, you can safeguard the healthy balance of your gut microbiota.
Key Takeaways on The Importance of Men's Gut Health
Foundation of Well-being: Gut health is integral to overall mental and physical well-being. It's not just about avoiding digestive discomfort; it impacts nutrient absorption, energy levels, mental clarity, appetite control, libido, and immune defenses.
Hormonal Harmony: The gut significantly influences hormonal balance, including appetite-regulating hormones, insulin for metabolism, and reproductive hormones like testosterone. Optimal gut health fosters muscle growth, regulates fat distribution, and supports libido.
Mental Clarity and Physical Performance: A well-functioning gut enhances cognitive function, mood, and quality of sleep. It also supports physical performance by aiding in nutrient absorption and energy metabolism.
Immune Strength: The gut houses a large portion of the immune system. A healthy gut microbiome defends against inflammation, pathogens, and chronic diseases, reinforcing immune defenses.
Actionable Steps for Gut Health: Men can improve gut health by diversifying their diet with fiber-rich foods, incorporating probiotics and prebiotics, staying hydrated, managing stress, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotics and over-the-counter drugs.



